Learn MongoDB in a nutshell
The following topics will be covered in this article:
- Insert Document
- Update Data in collection
- Delete Data in collection
- Get All collections from Database
- Use Equal, Less than, Greater Than, Less than or Equal and Greater than or Equal operators
- And Clause, Or clause, Not clause, Between clause and Like clause
- Sort, Limit, Projection, Sum, Count, Min, Max, Avg, Date time, Join, Group By and Having Clause
Databases originated in the 1960s in order to replace the existing file organization of data.
The first databases that appeared used hierarchical (tree-like) or network structures to store data.
Types of Databases:
SQL: Structured Query language is the standard language for dealing with Relational Databases. In this Data uses schemas and relations and will be scaled in vertical.
Important characteristics of the Databases:
- Structured data
- Related data
- Metadata
- Data integrity & Data security
- Data storage, retrieval, and update
NoSQL: Not only SQL, It schemas less and no relations (very few) data maintains. It’s possible to do horizontal and vertically data scaling. It stores and processes huge volumes of data
Important characteristics of the NoSQL Databases:
- Need to store unstructured data
- Need for scalability and flexibility
- Need for real-time access.
- Types of NoSQL Databases:
The following main types of NoSQL databases can be identified, depending on the data model used:
- Key-value store
- Document store
- Column-oriented
- Graph-oriented
The characteristics of the most popular products from each category are taken into account when performing the analysis. These are:
- Redis for key-value stores;
- MongoDB for document stores;
- Apache Cassandra for column-oriented stores;
- Neo4j for graph-oriented stores.
MongoDB is a No SQL database. It is an open-source, cross-platform, document-oriented database written in C++.
Why Use Mongo DB:
Please look into the below snapshot for better understanding :
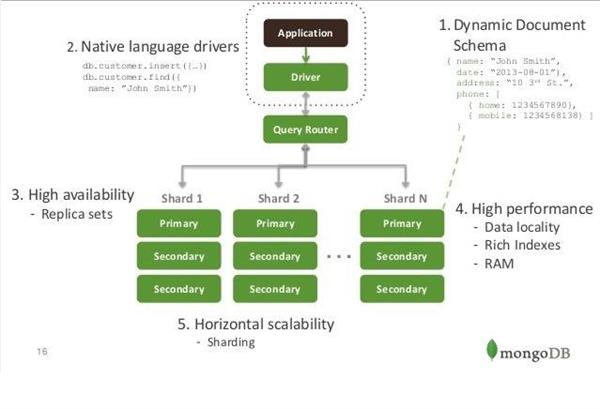
We can interact with MongoDB in different ways. Listed below
- Uses mongo shell to insert data and perform query operations.
- Uses MongoDB Compass to connect to insert data and perform query operations.
Here is the below link for more details.
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/getting-started/#getting-started
3. Here is the list of most popular third party MongoDB tools
- MongoBooster
- RoboMongo
- MongoVUE
- RockMongo
- MongoHub
- UMongo
- 3T Mongo Chef
Configuration through Mongo Shell
If you use “mongo” in the command prompt without configuring it, then it would give an error. Hence, configure it first.
Step 1: Go to the local disk C and get into Program Files. There you'll find a folder named MongoDB.
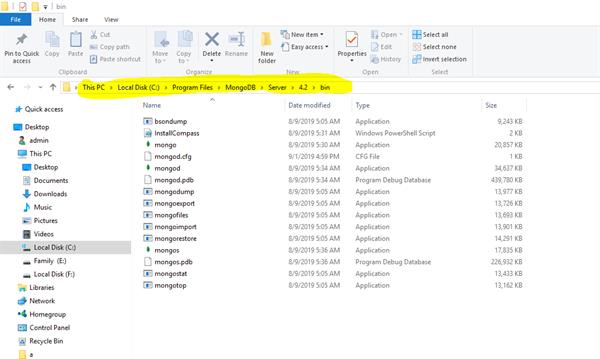
This is the following Path:
C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.2\bin\
Open Command prompts and types “mongod” to start the service.
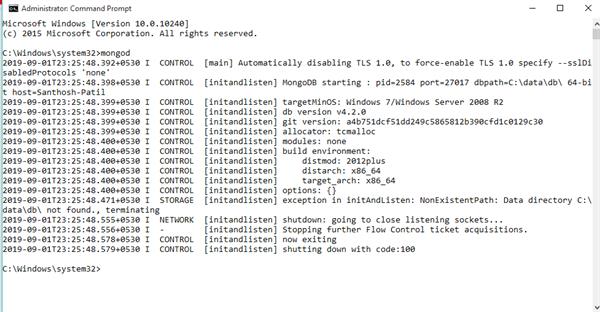
MongoDB requires a data directory to store all data. Mongo DB’s default data directory path is:
\data\db.
Create this folder
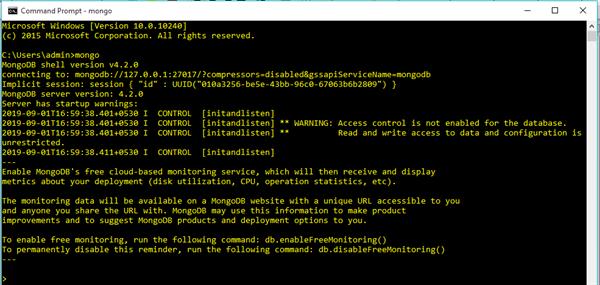
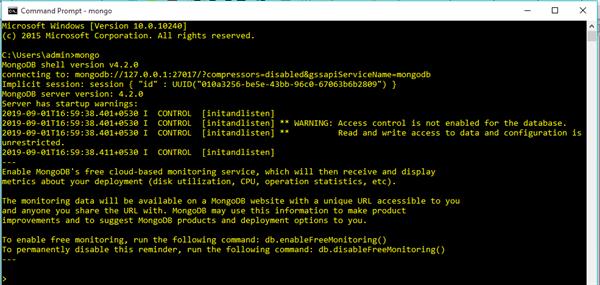
Write command on the command prompt “mongo” to create the connection.
MongoDB – Create Database
Creation of a database is so easy. All you have to do is to put “use” before the name of the database and press Enter.
First Create Connection:
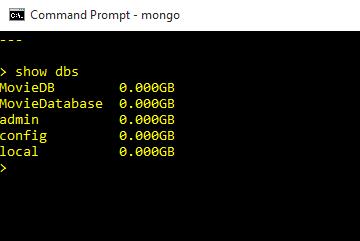
Mongo list collections with the command “show dbs”
As we have created a database. Now, let's create a mongo collection in it. For this purpose, a user must insert certain records which make up a mongo document in collection i.e. via Field Names & Field Values.
Connect to a MongoDB instance running on your localhost with default port 27017.
Create New Database:
Create a database with the name is MovieDatabase. This database has 2 collections: Movie collection and Product collection. Movie collection and Region collection have a One to Many. One movie can have many products and One region belongs to one and only one category.
/* Create MovieDatabase database */
use MovieDatabase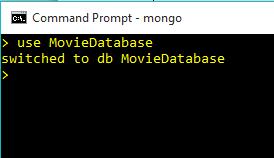
/* Create Movie collection */
db.createCollection('Movie');
/* Dumping data for ` movie ` collection */
db.getCollection('movie').insert({
name: 'Hollywood'
})
db.getCollection('movie').insert({
name: 'Bollywood'
})
db.getCollection('movie').insert({
name: 'Tollywood'
})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.movie.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5d6e06066f480eca73e15f22"), "name" : "Hollywood" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5d6e06106f480eca73e15f23"), "name" : "Bollywood" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5d6e061b6f480eca73e15f24"), "name" : "Tollywood" }
> 
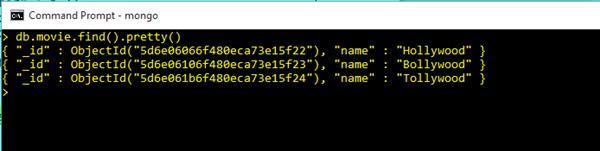
db.movie.find().pretty()
/* Create Region collection */
db.createCollection('region');
/* Dumping data for `` collection */
db.getCollection('region').insert({
FileName: 'Sahoo',
Budget: '350',
Language: 'Telugu',
date: ISODate('2019-08-30'),
movieId: ObjectId('5d6e061b6f480eca73e15f24'),
Industry: {
_id: new ObjectId(),
name: 'Tollywood'
}
});
db.getCollection('region').insert({
FileName: 'Bahuballi',
Budget: '200cr',
Language: 'Hindi',
date: ISODate('2015-08-30'),
movieId: ObjectId("5d6e06106f480eca73e15f23"),
Industry: {
_id: new ObjectId(),
name: 'Bollywood'
}
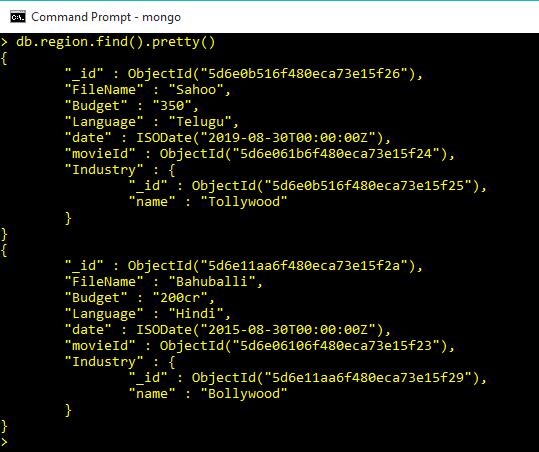
});db.region.find().pretty()
Update Data in collection
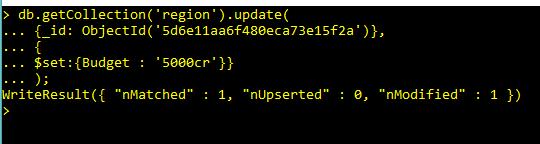
db.getCollection('region').update(
{_id: ObjectId('5d6e11aa6f480eca73e15f2a')},
{
$set:{Budget : '5000cr'}}
);
Check now the collection is updated or not
db.region.find().pretty()
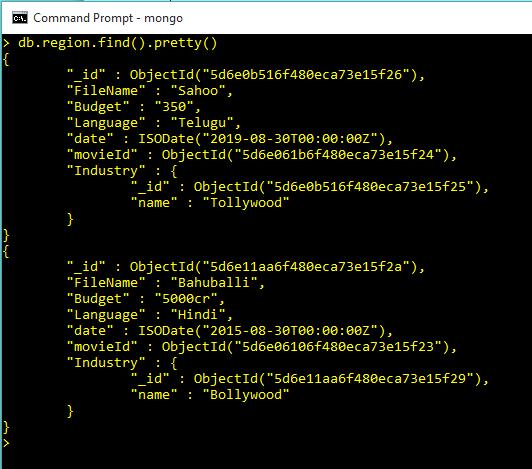
Delete Data in Collection
db.getCollection('region').remove({_id: ObjectId('5d6e11aa6f480eca73e15f2a')});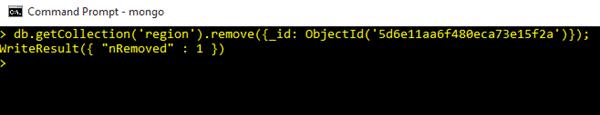
Check now particular id collection is deleted or not
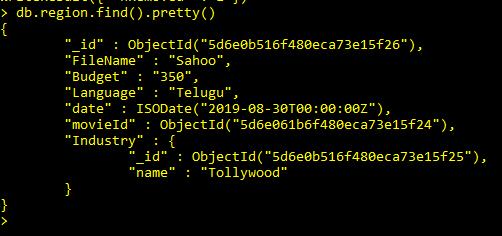
Get All collections from Database
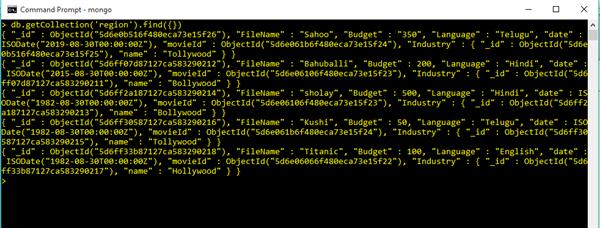
Add some movies to the collections for better understanding.
db.getCollection('region').find({})Use find() method display documents in Region Collection
Use Equal Operator in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({Language: 'Hindi'})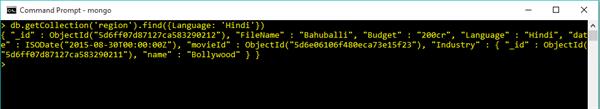
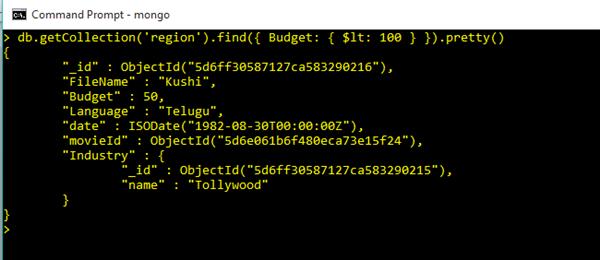
Use Less Than Operator in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ Budget: { $lt: 100 } })Output
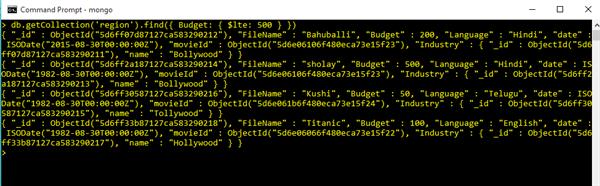
Use Less Than or Equal Operator in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ Budget: { $lte: 500 } })Output
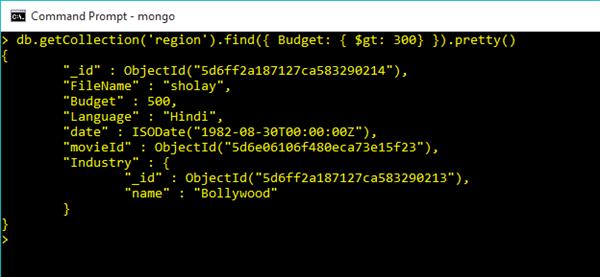
Use Greater Than Operator in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ Budget: { $gt: 300} })Output
Use Greater Than or Equal Operator in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ Budget: { $gte: 300 } })Output
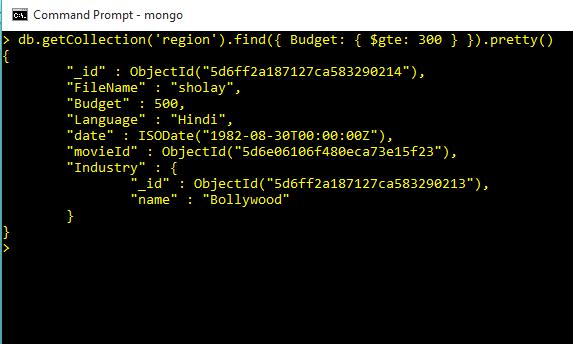
And Clause in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ $and: [{Budget: {$lt: 200}}, {Language: "English"}] }).pretty()Output
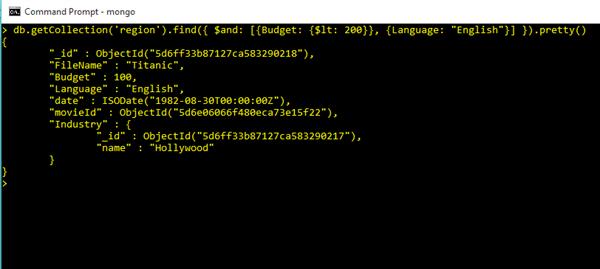
Or Clause in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ $or: [{Budget: {$gt: 2200}}, {Language: "Telugu"}] }).pretty()Output
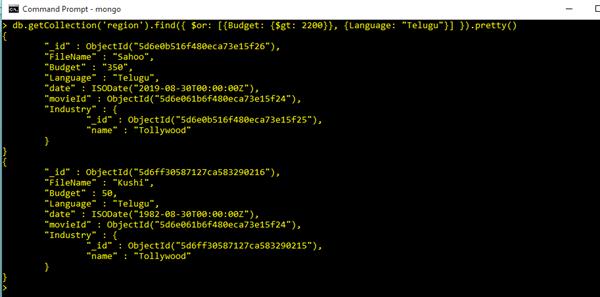
Not Clause in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ Language: { $ne: "Hindi" } }).pretty()
Output.
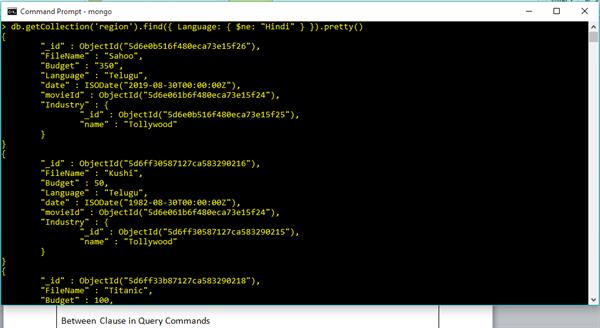
Between Clause in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({ $and: [{Budget: {$gte: 100}}, { Budget: {$lte: 300}}] }).pretty()Output
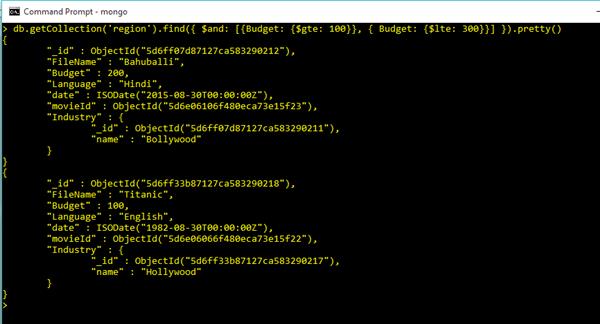
Like Clause in Query Commands
Start with Mob string
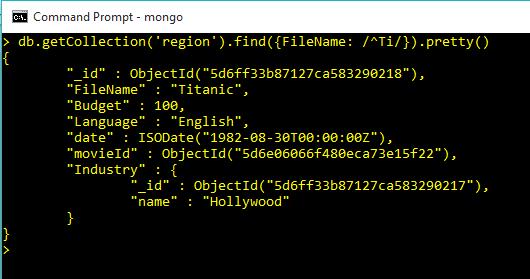
db.getCollection('region').find({FileName: /^Ti/}).pretty()Output
Ends with le 2 string
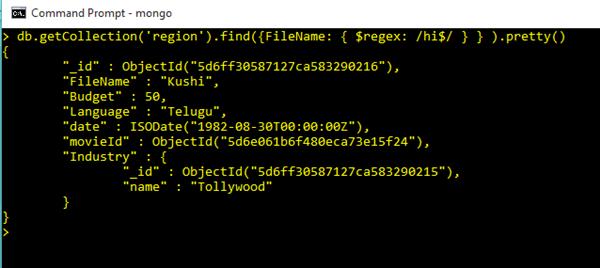
db.getCollection('region').find({FileName: { $regex: /hi$/ } } ).pretty()Output
Limit in Query Commands
If we want to fetch the first two documents from the collection "region", the following MongoDB command can be used
db.region.find().limit(2).pretty();If we want to fetch two documents after the first two documents from the collection 'region', the following MongoDB command can be used :
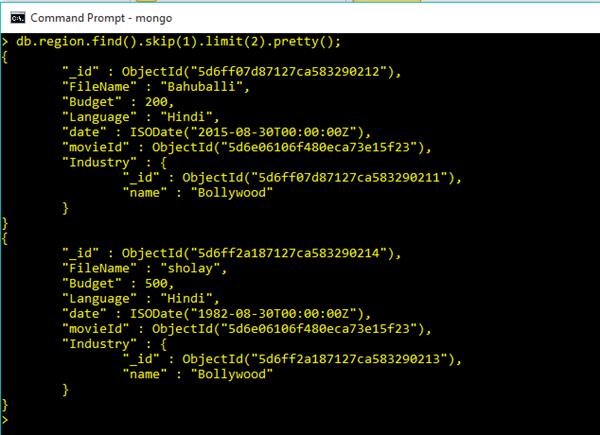
db.region.find().skip(2).pretty();If we want to fetch the two documents after the first document from the collection 'region', the following MongoDB command can be used :
db.region.find().skip(1).limit(2).pretty();Output
Sort by Budget Ascending
db.getCollection('region').find().sort({Budget: 1})Output
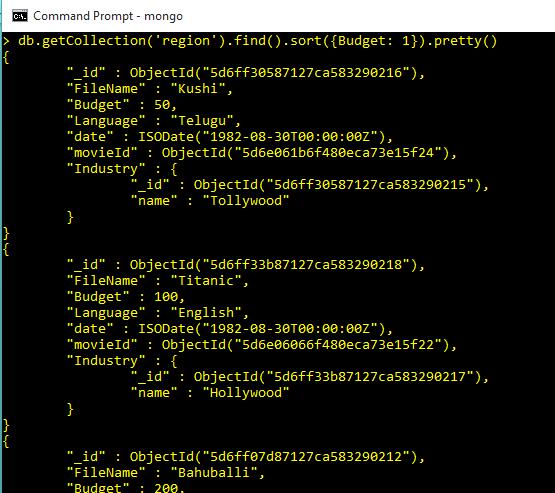
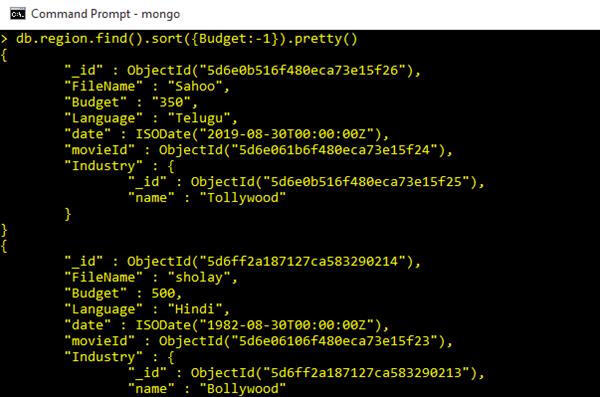
Sort by Budget Descending
db.region.find().sort({Budget:-1}).pretty()Output
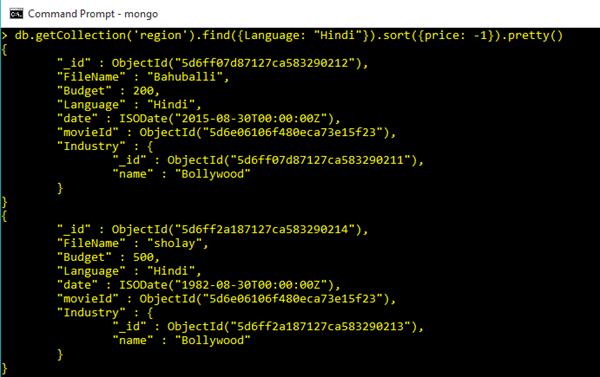
Sort and Condition
db.getCollection('region').find({Language: "Hindi"}).sort({price: -1})Output
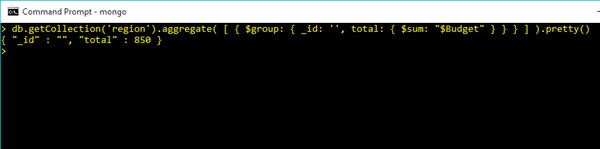
Sum in Query Commands
Sum Budget
db.getCollection('region').aggregate( [ { $group: { _id: '', total: { $sum: "$Budget" } } } ] ).pretty()Output
db.getCollection('region').aggregate([
{
$match: {
$and: [{Budget: {$lt: 200}}, {Language: "English"}] }
},
{
$group: { _id: '', total: { $sum: "$Budget" } }
}
]).pretty()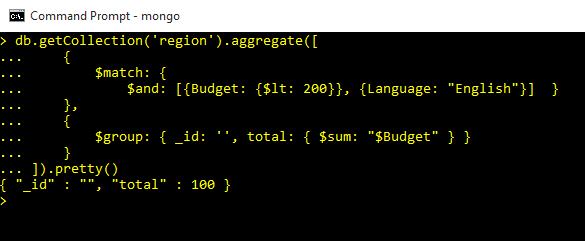
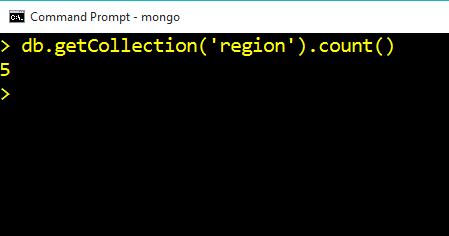
Count Product in Query Command
db.getCollection('region').count()
Output
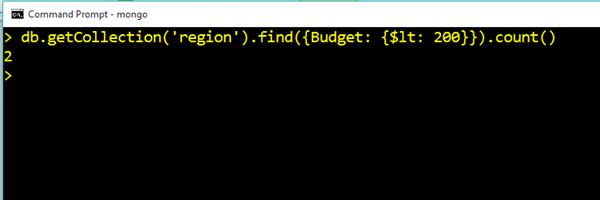
Sum Budget With Conditions
db.getCollection('region').find({Budget: {$lt: 200}}).count()Output
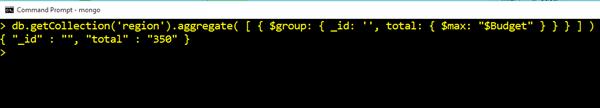
Min and Max in Query Commands
The Biggest Price
db.getCollection('region').aggregate( [ { $group: { _id: '', total: { $max: "$Budget" } } } ] )Output
The Smallest Budget
db.getCollection('region').aggregate( [ { $group: { _id: '', total: { $min: "$Budget" } } } ] )Output
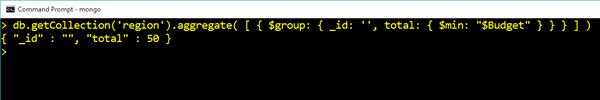
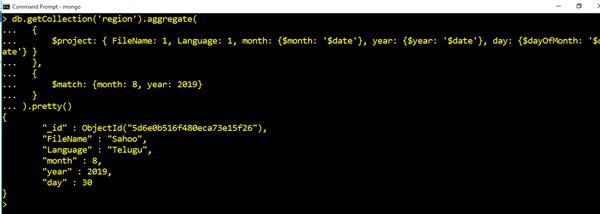
Use Date and Time with Conditions
db.getCollection('region').aggregate(
{
$project: { FileName: 1, Language: 1, month: {$month: '$date'}, year: {$year: '$date'}, day: {$dayOfMonth: '$date'} }
},
{
$match: {month: 8, year: 2019}
}
).pretty()Output
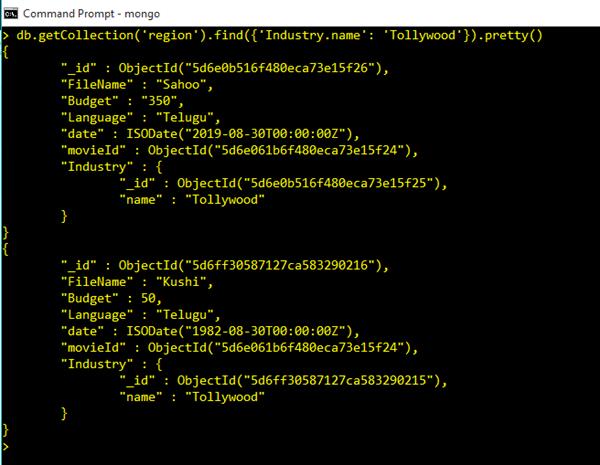
Filter Data with Embed Document in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').find({'Industry.name': 'Tollywood'}).pretty()Output
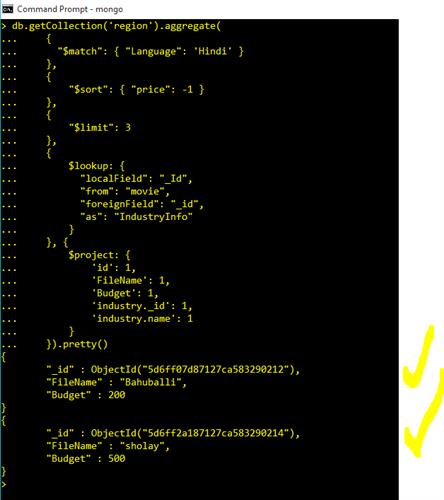
Join and Conditions in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').aggregate(
{
"$match": { "Language": 'Hindi' }
},
{
"$sort": { "price": -1 }
},
{
"$limit": 3
},
{
$lookup: {
"localField": "_Id",
"from": "movie",
"foreignField": "_id",
"as": "IndustryInfo"
}
}, {
$project: {
'id': 1,
'FileName': 1,
'Budget': 1,
'industry._id': 1,
'industry.name': 1
}
}).pretty()
Output
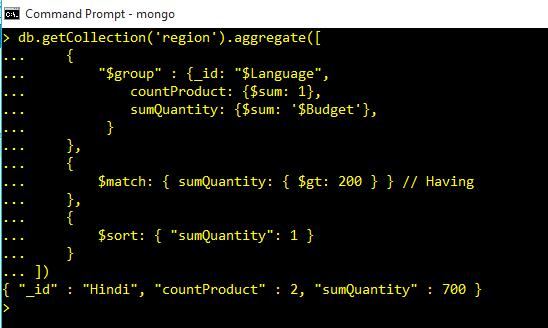
Group By and Having in Query Commands
db.getCollection('region').aggregate([
{
"$group" : {_id: "$Language",
countProduct: {$sum: 1},
sumQuantity: {$sum: '$Budget'},
}
},
{
$match: { sumQuantity: { $gt: 200 } } // Having
},
{
$sort: { "sumQuantity": 1 }
}
]).pretty()Output :
MongoDB Compass GUI
MongoDB Compass to connect to insert data and perform query operations. Once downloaded and open MongoDB Compass, Need to fill below details for connecting mongo DB host. Here right up corner, we have connection and disconnection options for connecting host.
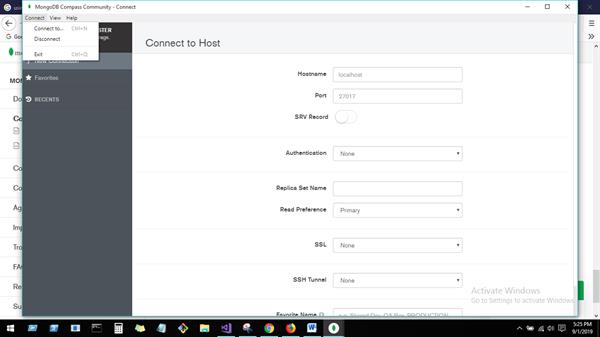
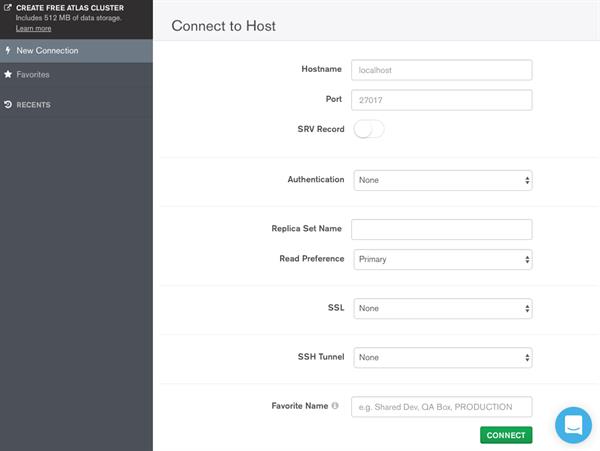
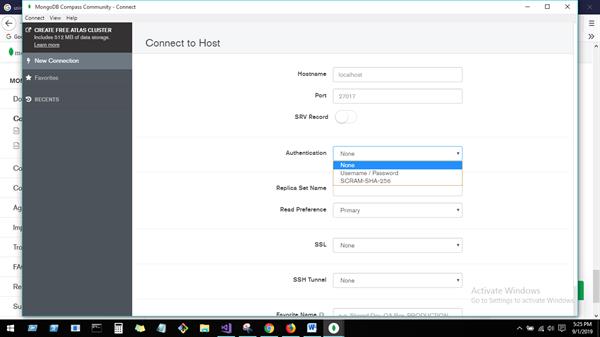
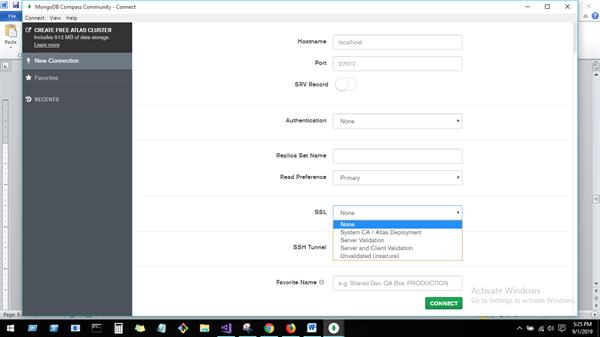
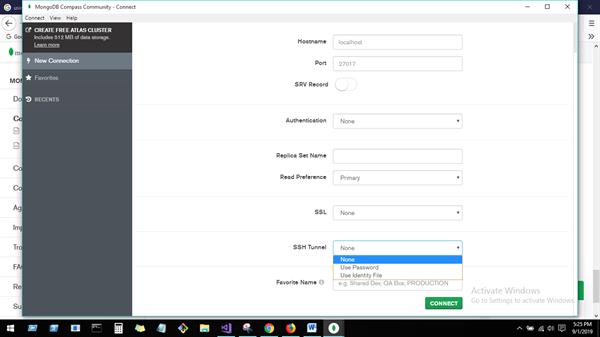
You can create Database from this UI.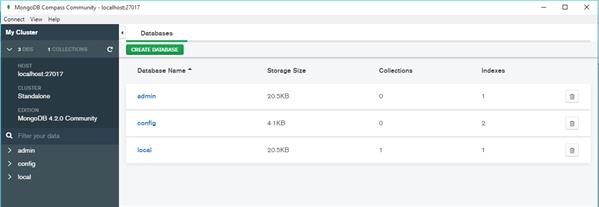
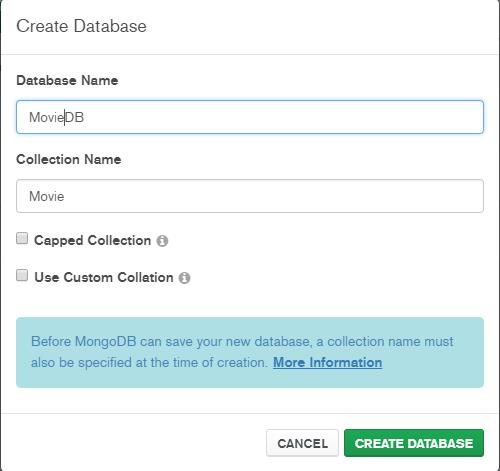
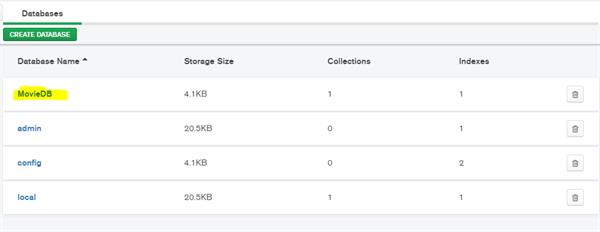
Here you can create collections (tables).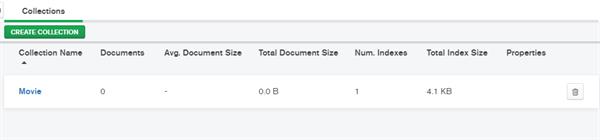
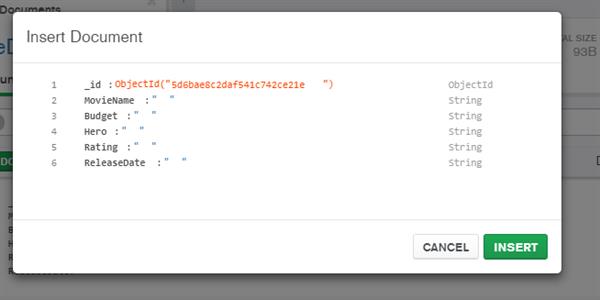
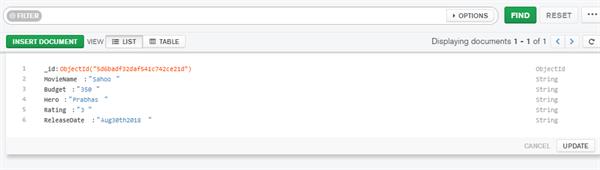
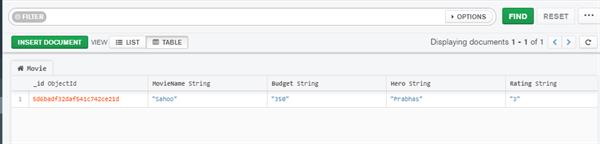
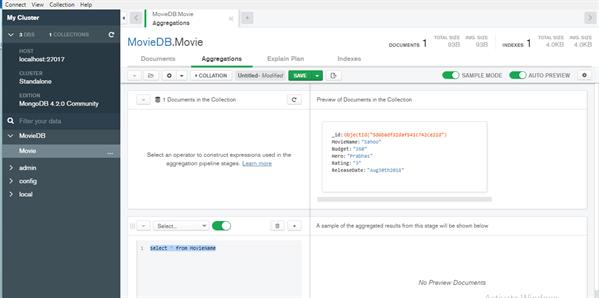
Here point out to environments pipeline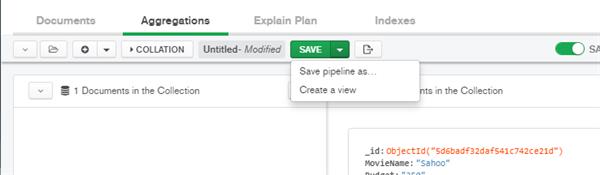
Hope this article will help you.
Thanks





