Data Recovery
Data recovery is the process of restoring data that has been lost accidentally deleted, corrupted and inaccessible.
Storage Structure
Storage structure is the memory structure mainly divided into two categories:
- Volatile Memory: - These are the primary memory, and are placed along with the CPU. These memories use to store only small amount of data, but these memory are very fast.
Example. - Main memory, cache memory etc. these memories cannot endure system crashes- data in these memories will be lost during failure.
- Non-Volatile memory: - These are secondary memories and are huge in size but processing is very slow.
Example. Flash memory, hard disk, magnetic tapes etc. these memories are designed to withstand system crashes.
- Stable Memory: - This is known to be third form of memory structure but it is similar as non-volatile memory. In this case, copies of same non-volatile memories are stored at different places. This is because, in the case of data loss, data can be recovered from other copies.
Failure Classification and Recovery
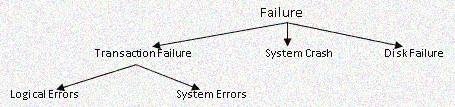
Transaction failure
This is the condition where a transaction fails to execute and it reaches a point from where it can’t go any further. This is called transaction failure where only a few transactions or processes are hurt and failure can be cause of logical errors in the code or System error.
System Crash: -
This can be because of hardware or software failure or due to external factors like power cut. In most of the cases data in the secondary memory are not affected because of this crash. This is because; the database has lots of integrity checkpoints to prevent the data loss from secondary memory.
Disk Failure: -
These are the problems with hard disks like formation of bad sectors, disk head crash, unavailability of disk etc.
Data recovery techniques
Instant recovery is also known as recovery in place it tries to eliminate the recovery window by redirecting user workloads to the backup server. A snapshot is created so the backup remains in a pristine state and all user write operations are redirected to that snapshot; users then work off the backup VM (virtual machine) and the recovery process begins in the background. Users have no idea the recovery is taking place, and once the recovery is complete, the user workload is redirected back to the original VM.
One way to avoid the time-consuming and costly process of data recovery is to prevent the data loss.
Data loss prevention (DLP) products help companies to identify and stop data leaking.



