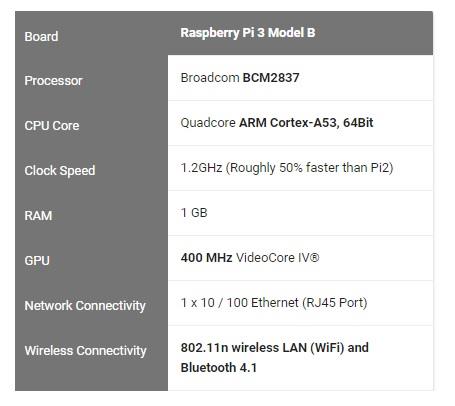
Raspberry Pi 3 Hardware Specification
OS supported by Raspberry Pi 3:
- Raspbian
- CentOS
- Fedora
- Ubuntu MATE
- Kali Linux
- Ubuntu Core
- Windows 10 IoT Core
- RISC OS
- Slackware
- Debian
- Arch Linux ARM
- Android Things
- SUSE
- FreeBSD
- NetBSD
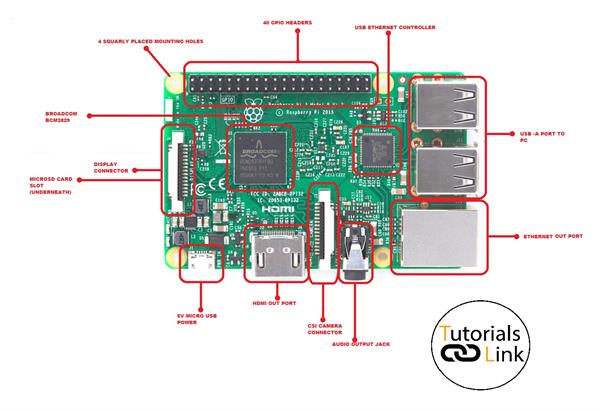
Specifications of the Raspberry Pi 3:
- 4 USB ports
- 40 GPIO pins
- Full HDMI port
- Ethernet out port
- Combined 3.5mm audio jack and composite video
- Camera interface (CSI)
- Display interface (DSI)
- Micro SD card slot
- 5v Micro USB port
- Broadcom BCM2829
- USB Ethernet Controller
- Mounting Holes
4 USB ports:
Raspberry Pi has 4 USB ports for connecting external devices such as pendrives, mouse and keyboard etc.
40 GPIO pins:
40 GPIO pins are general purpose input output pins that is used to take input and output from different sensors and devices we will discuss about this in brief later.
HDMI port:
HDMI port is provided for connecting different display devices to Raspberry Pi.
Ethernet port:
Ethernet port is provided for connecting internet via LAN port in Raspberry Pi.
Audio Jack:
Audio jack is provided to route audio to external devices or provide audio input to Raspberry Pi.
Camera interface (CSI):
CSI port is provided to connect camera to Raspberry Pi for image processing and other stuff.
Display interface (DSI):
Display interface port is provided to connect display to Raspberry Pi.
Micro SD Card Slot:
Micro SD Card Slot is used for inserting external micro SD card in Raspberry Pi.
5v Power supply:
5v power supply port is provided to connect power source via cable.
Broadcom BCM2829:
The Broadcom BCM2837 system-on-chip (SoC) includes four high-performance ARM Cortex-A53 processing cores running at 1.2GHz with 32kB Level 1 and 512kB Level 2 cache memory.
USB Ethernet controller:
USB Ethernet controller chip is used to manage connection and route the connection via Ethernet.
Mount Holes:
Mount holes are holes provided on every corner of Raspberry Pi to fit in different covers available in markets.
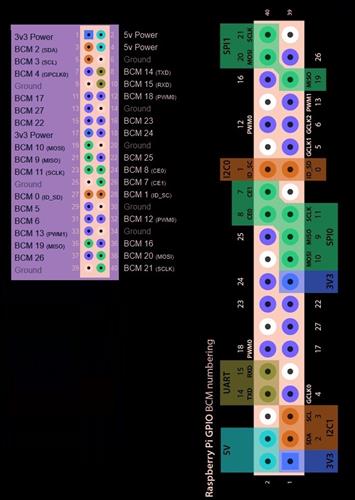
Pins and Raspberry:
Pins differ from board to board; different boards can have different pin configuration and number of pins.
GPIO pins or general-purpose input/output pins are one of reason for popularity of single board computers.
Types of Pins in Raspberry Pi:
· GPIO
· POWER
· GROUND
· UART
· DPI
· I2C
GPIO Pins:
GPIO pins can be used in two ways:
· For taking input from different input sensors like LDR
· For giving output to different devices like led
As the name itself define its use, they are general purpose pins which enables the user to configure it and use it accordingly.
Power Pin:
Power Pins are pins that provide 5V power that can be used to power different devices or sensors.
Ground Pin:
Ground pins provide ground to the circuit can be used to provide ground to different sensors or devices.
UART:
Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter is a set of communication pins provided in Raspberry Pi for sending and receiving data wired or wirelessly.
UART include set of two pins are RX and TX which are used for receiving and transmitting data serially respectively.
I2C Pins:
2C is a multi-master bus, which means that multiple chips can be connected to the same bus and each one can act as a master by initiating a data transfer. I2C is a very commonly used standard designed to allow one chip to talk to another. So, since the Raspberry Pi can talk I2C we can connect it to a variety of I2C capable chips and modules.
SPI Pins:
SPI pins are pins that enables Raspberry Pi to communicate with other microcontrollers and device.
SPI and I2C do the same function but SPI have a single master which control all slaves clock in the bus on the other hand I2C can have number of masters.



