What is Storage Provisioning in Virtualization Concepts?
What is Storage Provisioning in Virtualization Concepts?
The cost of managing data center storage can rise quickly when you consider the expense of purchasing new devices, along with operating costs such as energy expenses, as well as staff to monitor data capacity and maintain the hardware. Therefore, using and allocating storage in a data center needs to be done in the most efficient way possible without affecting reliability, making sure data is delivered to the customer. This section will focus on how data storage capacity is managed to get the most storage possible out of a device.
Provisioning is the process of strategically assigning storage space to servers based on the capacity of the storage device(s), availability, and performance requirements. Storage provisioning can be performed in two ways, traditional (thick provisioning) and virtual (thin provisioning).
In order for a disk to be provisioned, the storage volumes are partitioned to create logical disks. Simply put, a logical disk is a virtualized disk. The capacity of a logical disk physically exists in a device somewhere, but the logical disk itself does not physically exist. Provisioning requires that disk space is turned into logical rather than physical units because physical disk space cannot be shifted around strategically as quickly as logical space can be. Remember, logical disks are data representations of physical disks, not physical hardware.
In traditional provisioning, also called thick provisioning, disk space is strategically pre-allocated to a server or a virtual machine. This means that the logical space provided by partitioning is equal to the amount of actual physical space set aside on the disk.
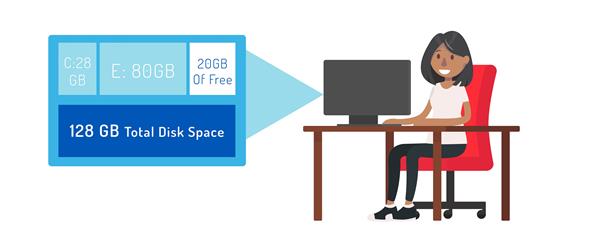
For example, when you set up an operating system like Windows, a certain amount of storage space is provisioned for certain files and programs. With this method, you first estimate how much storage the program will need for its entire life cycle. You then provision a fixed amount of storage space to the disk in advance, for example, in the image below, a 128GB hard drive has been provisioned to allow 28GB for the C drive and 80GB for the E drive, leaving 20GB of free space. Both the C and E drives have been thick provisioned. This is demonstrated by the storage space provided in advance in anticipation that each drive will need that amount to meet future storage needs.