Getting Started With Blazor Using ASP.NET Core
Introduction
Microsoft has recently announced the release of a new .NET web framework – Blazor. In this article, we will understand Blazor and setup Blazor development environment in our machine and execute our first program in ASP.NET core using Blazor and Visual Studio 2017. We will also create a sample calculator application using Blazor.
What is Blazor?
Blazor is a new .NET web framework for creating client-side applications using C#/Razor and HTML that runs in the browser with WebAssembly. It can simplify the process of creating single page application (SPA) and at the same time enables full stack web development using .NET.
Using .NET for developing Client-side application has multiple advantages that are mentioned below,
- .NET offers a range of API and tools across all platform that are stable and easy to use.
- The modern languages such as C# and F# offer a lot of features that make programming easier and interesting for developers.
- The availability of one of the best IDE in form of Visual Studio provides a great .NET development experience across multiple platforms such as Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
- .NET provides features such as speed, performance, security, scalability, and reliability in web development that makes full stack development easier.
Prerequisites
The Blazor is not supported on versions below Visual Studio 2017 v15.7
Source Code
Before proceeding I would recommend you to get the source code from Github
Getting Started with Blazor
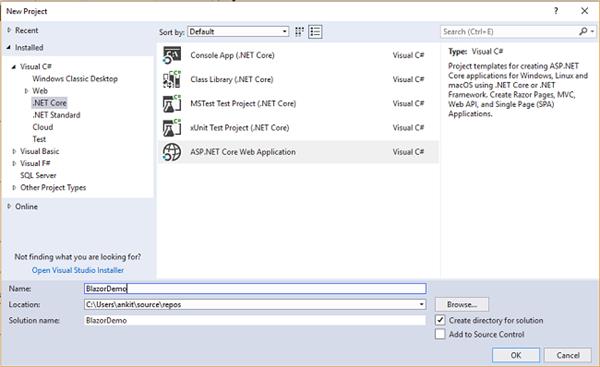
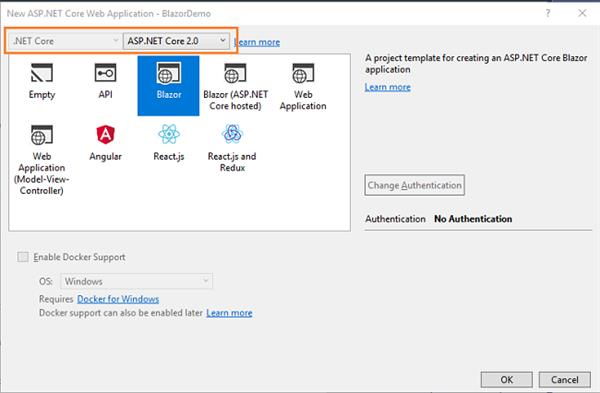
To create our first Blazor application we need to install "ASP.NET Core Blazor Language Services extension" from here.Open Visual Studio and select File >> New >> Project. After selecting the project, a "New Project" dialog will open. Select .NET Core inside Visual C# menu from the left panel. Then, select “ASP.NET Core Web Application” from available project types. Put the name of the project as BlazorDemo and press OK.
Create a Sample Calculator Using Blazor
We are going to create a basic calculator app, which is able to do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Right click on Pages folder and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select Web from the left panel, then select “Razor View” from templates panel and put the name as Calculator.cshtml. Press OK.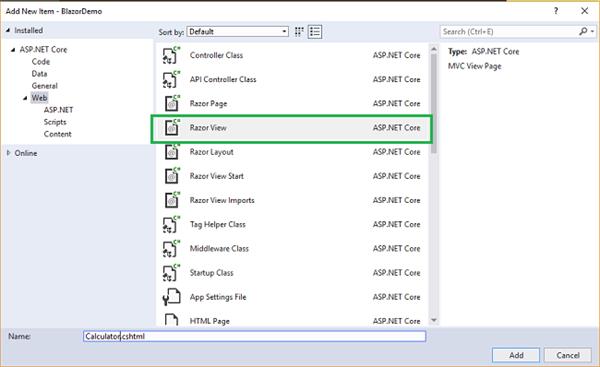
@page "/calculator"
<h1>Basic Calculator Demo Using Blazor</h1>
<hr />
<div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-3">
<p>First Number</p>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input placeholder="Enter First Number" @bind(num1)>
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-3">
<p>Second Number</p>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input placeholder="Enter Second Number" @bind(num2)>
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-3">
<p>Result</p>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input readonly @bind(finalresult)>
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @onclick(AddNumbers) class="btn">Add (+)</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @onclick(SubtractNumbers) class="btn btn-primary">Subtract (−)</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @onclick(MultiplyNumbers) class="btn btn-success ">Multiply (X)</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @onclick(DivideNumbers) class="btn btn-info">Divide (X)</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@functions {
string num1;
string num2;
string finalresult;
void AddNumbers()
{
finalresult = (Convert.ToDouble(num1) + Convert.ToDouble(num2)).ToString();
}
void SubtractNumbers()
{
finalresult = (Convert.ToDouble(num1) - Convert.ToDouble(num2)).ToString();
}
void MultiplyNumbers()
{
finalresult = (Convert.ToDouble(num1) * Convert.ToDouble(num2)).ToString();
}
void DivideNumbers()
{
if (Convert.ToDouble(num2) != 0)
{
finalresult = (Convert.ToDouble(num1) / Convert.ToDouble(num2)).ToString();
}
else
{
finalresult = "Cannot Divide by Zero";
}
}
} Let’s understand this code. On the top, we are defining the route of this page using @page directive. So in this application, if we append “/calculator” to base URL then we will be redirected to this page.
Then we have defined the HTML section to read two numbers from the user and display the result in another textbox. The attribute “@bind” is used to bind the value entered in the textbox to the variables we have defined. We also created four buttons to perform our basic arithmetic operations. We are calling our business logic methods on button click.
Finally, we will add the link to our “calculator” page in the navigation menu, open /Shared/NavMenu.cshtml page and put the following code into it.
<div class='main-nav'>
<div class='navbar navbar-inverse'>
<div class='navbar-header'>
<button type='button' class='navbar-toggle' data-toggle='collapse' data-target='.navbar-collapse'>
<span class='sr-only'>Toggle navigation</span>
<span class='icon-bar'></span>
<span class='icon-bar'></span>
<span class='icon-bar'></span>
</button>
<a class='navbar-brand' href='/'>BlazorDemo</a>
</div>
<div class='clearfix'></div>
<div class='navbar-collapse collapse'>
<ul class='nav navbar-nav'>
<li>
<NavLink href="/" Match=NavLinkMatch.All>
<span class='glyphicon glyphicon-home'></span> Home
</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink href="/counter">
<span class='glyphicon glyphicon-education'></span> Counter
</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink href="/fetchdata">
<span class='glyphicon glyphicon-th-list'></span> Fetch data
</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink href="/calculator">
<span class='glyphicon glyphicon-th-list'></span> Calculator
</NavLink>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
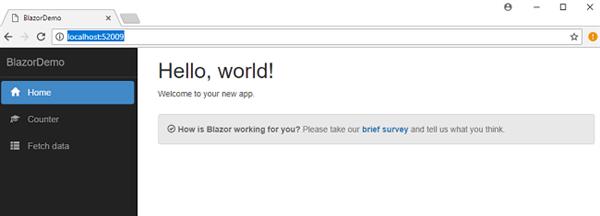
</div> Execution Demo
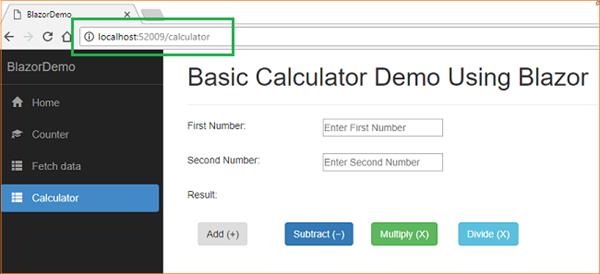
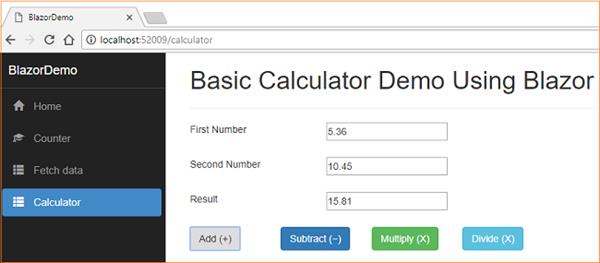
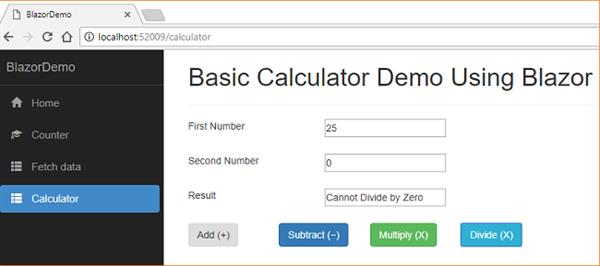
Conclusion
We learned about the new .NET framework – Blazor. We have also created a simple calculator application using Blazor and performed arithmetic operations on it.You can also fork this application on Github. Try this new framework and let me know what you think of it in the comments section below.





