Get Started with Microsoft Azure Step by Step
Following are the topics that covered in this Article:
- Introduction to cloud computing
- Overview of Microsoft Azure
- Azure Services
- Azure Subscriptions
- Management Groups, Resource Manager
- Azure Portal
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is typically defined as a type of computing that relies on on-demand computing resources (network, servers, storage, services - computers that share resources) rather than having local servers.
Advantages of the cloud:
- Elasticity: an organization is able to scale very quickly to thousands of machines
- Costs: reducing upfront IT costs and eliminate the need for technical personnel to maintain servers and local infrastructure
- Backups and HA: most cloud providers have high availability and SLA of 99.999%
- Gives the best Performance and Scalability.
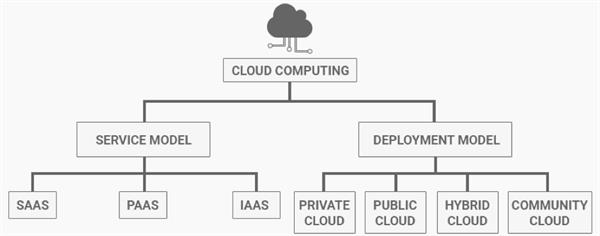
Cloud Service models:
In given below the cloud service model, the cloud hosting providers offers the user to access their systems through software. The user installs software applications on their local device. Instead of application sometimes they use web API to access the cloud. Through the application, the user can store, analysis and collaborate with a cloud server.
Cloud Service models are mainly three types. Those three types of cloud service models are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. As a result, cloud service models help in different ways. They are basically used to send data or use applications from the cloud. Data are stored in Cloud Storage.
Cloud storage is a redundant data server at various locations. The cloud service model helps to transfer data. We have discussed earlier algorithms of cloud computing.
Service Models of the Cloud:
The service model is defined based on the type of cloud services that it offers. It includes three types of cloud services known as SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS.
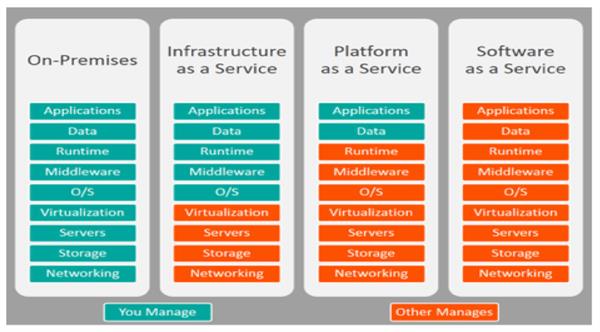
- SAAS:
-
- It stands for “Software as a Service”.
- SAAS allows users to run existing online software applications that are accessed over the internet.
- Some examples of SaaS are Office 365, Salesforce
- PAAS :
-
- It stands for “Platform as a Service”.
- PAAS allows users to create and run their own cloud applications using supplier-specific tools and languages. It is mainly designed for developers to test or run codes and applications.
- Some examples of PAAS are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine, Apache.
- IAAS :
-
- It stands for “Infrastructure as a Service”.
- IAAS allows users to run any applications they want on cloud hardware of their own choice.
- IAAS Includes Cloud services like Servers, Storage, Networking, Firewall, Load Balancer, etc.
- Some examples of IAAS are Amazon, Microsoft Azure, Google, etc
With this Following Image, you can understand more:
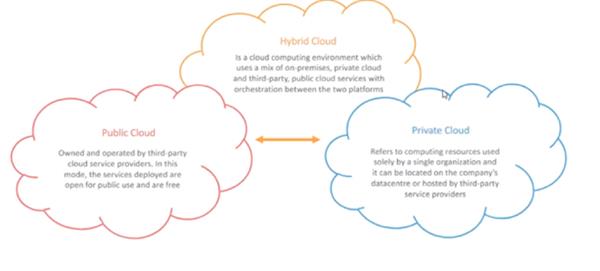
Deployment Model:
The deployment model is based on the type of deployment which is followed. It includes four types of cloud i.e. Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, and Community Cloud.
Microsoft Azure:
Azure is Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, providing a variety of services that can be used without purchasing or provisioning hardware.
Azure enables the rapid development of solutions and provides the resources to accomplish tasks that may not be feasible in an on-premise environment. Azure’s compute, storage, network and application services can also be used in a hybrid configuration, connecting on-premise infrastructure with the Microsoft Cloud.
Now let’s have a look at the benefits that the Microsoft Azure services in India offer to the businesses:
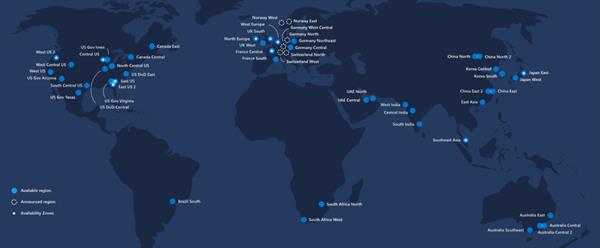
Azure regions:
Azure has more global regions than any other cloud provider – offering the scale needed to bring apps closer to users around the world, preserving data residency and offering comprehensive compliance and resiliency options for customers.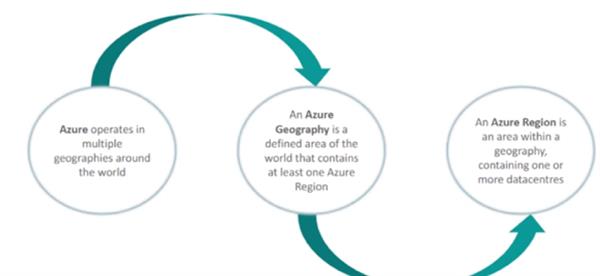
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/global-infrastructure/regions/
Azure Portal:
Build, manage and monitor everything from simple web apps to complex cloud applications in a single, unified console.
- Create your Azure free account as below mentioned URL.
- Get started with 12 months of free services
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/features/azure-portal/

Home Page: https://portal.azure.com/#home:
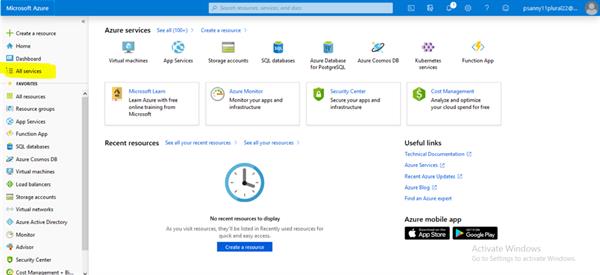
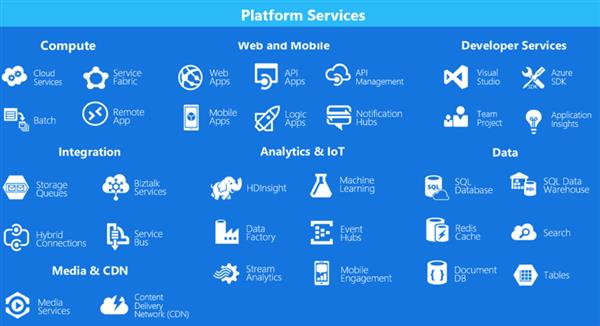
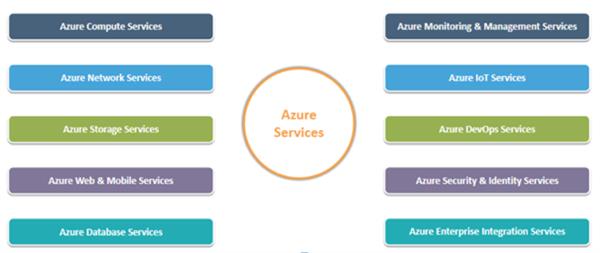
Azure Services:
Microsoft Azure offers so many services through its cloud computing platform. Some of them are listed in the fig.

Developer Tools :
Azure is well integrated with SDKs and developer tools to allow seamless development flow from project set up to deployment and resource management.
Azure SDKs :
Install the Azure SDK for an additional set of templates and tools which help you access even more cloud resources and services to improve your Azure development experience directly from Visual Studio. Use these tools to deploy infinitely-scalable applications and APIs, configure diagnostics, create and manage app service resources and integrate your data.
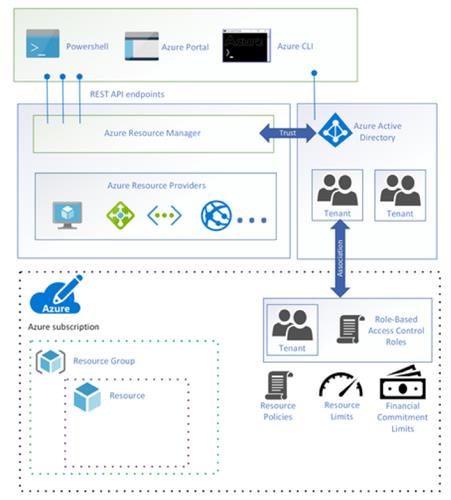
Azure Resource Manager Overview:
Azure Resource Manager is the deployment and management service for Azure. It provides a consistent management layer that enables you to create, update, and delete resources in your Azure subscription. You can use its access control, auditing, and tagging features to secure and organize your resources after deployment.
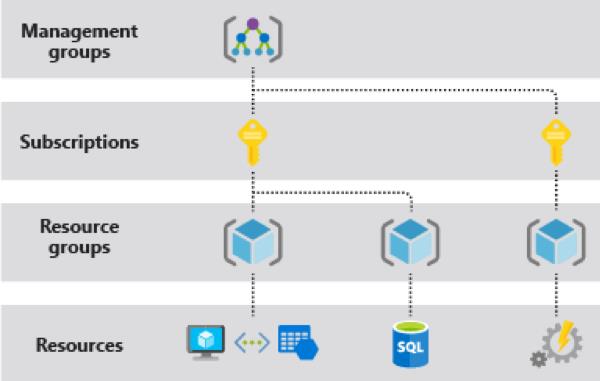
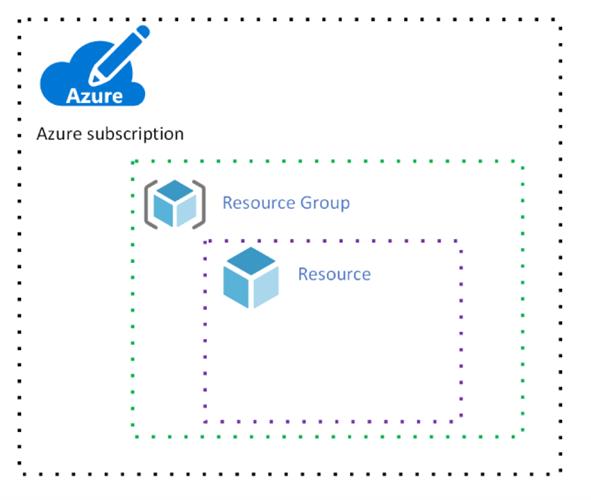
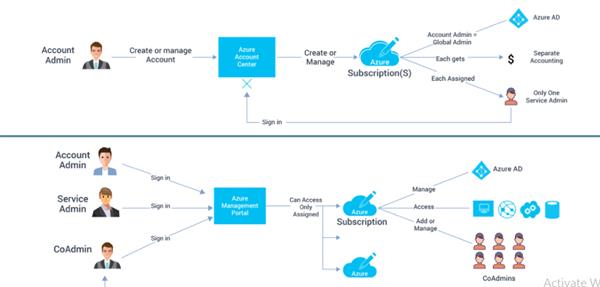
Azure Subscription :
In Microsoft Azure, subscriptions are tied to a particular account, with access to usage reporting and billing. Azure subscriptions establish the set of resources available to a user
Azure subscriptions establish three parameters: a unique subscriber ID, a billing location and a set of available resources.

|

|
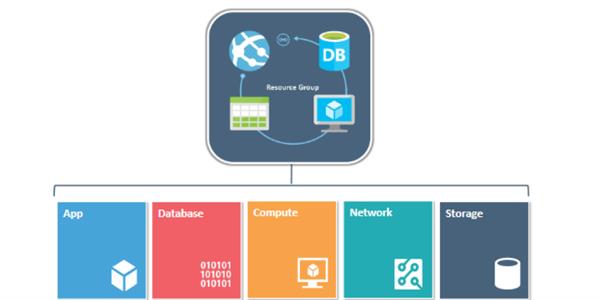
Azure Resource Group:
A container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. The resource group includes those resources that you want to manage as a group. You decide how to allocate resources to resource groups based on what makes the most sense for your organization.
Resource:
In Azure, the term resource refers to an entity managed by Azure. For example, virtual machines, virtual networks, and storage accounts are all referred to as Azure resources.
A manageable item that is available through Azure. Virtual machines, storage accounts, web apps, databases, and virtual networks are examples of resources.
How does Azure work?
Azure, like other cloud platforms, relies on a technology known as virtualization.
Essentially, the cloud is a set of physical servers in one or more data centers that execute virtualized hardware on behalf of customers.
To understand this, let's look at the architecture of the hardware in the datacenter.
Inside each datacenter is a collection of servers sitting in server racks. Each server rack contains many server blades as well as a network switch providing network connectivity and a power distribution unit (PDU) providing power. Racks are sometimes grouped together in larger units known as clusters.
Within each rack or cluster, most of the servers are designated to run these virtualized hardware instances on behalf of the user.
However, some of the servers run cloud management software known as a fabric controller. The fabric controller is a distributed application with many responsibilities. It allocates services, monitors the health of the server and the services running on it, and heals servers when they fail.
Each instance of the fabric controller is connected to another set of servers running cloud orchestration software, typically known as a front end. The front end hosts the web services, RESTful APIs, and internal Azure databases used for all functions the cloud performs.
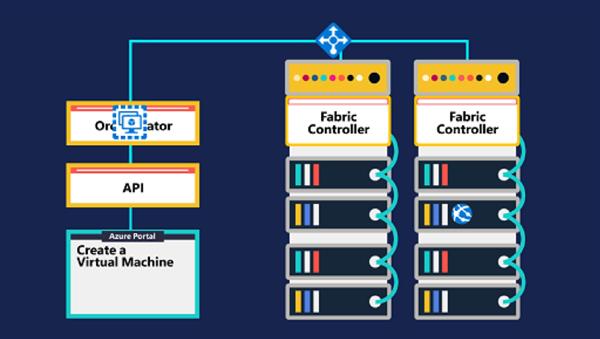
Begin by taking a closer look at how resources are deployed in Azure.
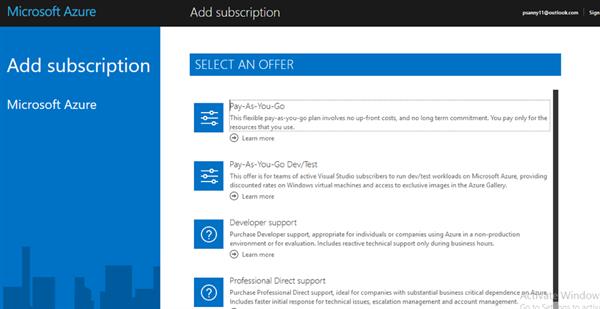
Login to your admin account on Azure Subscription and go to https://account.azure.com/Subscriptions
Now Click to Add Subscription.
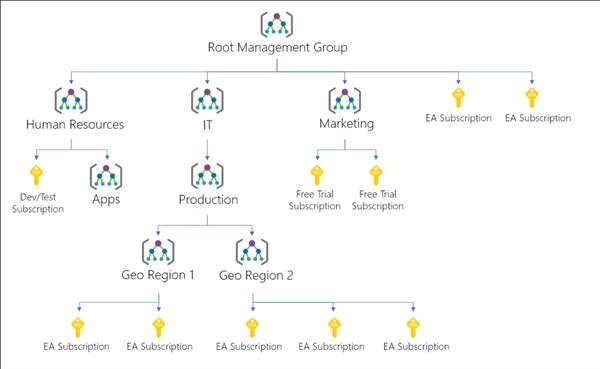
Azure Management Groups
Management groups allow you to organize your subscriptions and apply governance controls, such as Azure Policy and Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC), to the management groups. All subscriptions within a management group automatically inherit the controls applied to the management group. No matter if you have an Enterprise Agreement, Certified Solution Partner, Pay-As-You-Go, or any other type of subscription, this service gives all Azure customers enterprise-grade management at a large scale for no additional cost.
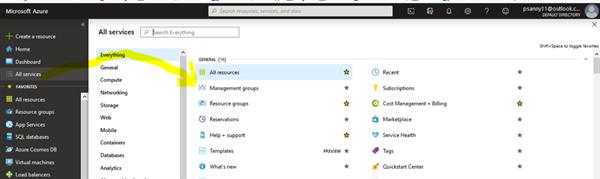
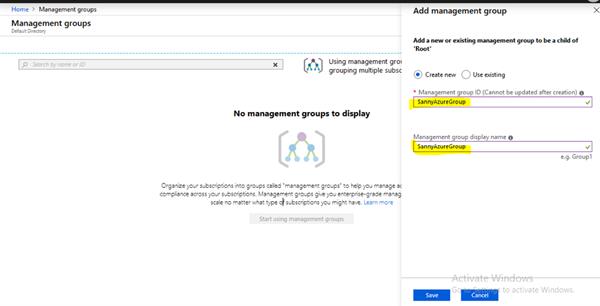
Azure Resource Manager
Deployment and Management service for azure that host the restful APIs and it is responsible for provisioning the resources.
ARM provides a consistent management layer to perform tasks through Azure PowerShell, CLI, portal and rest API, and client SDKs
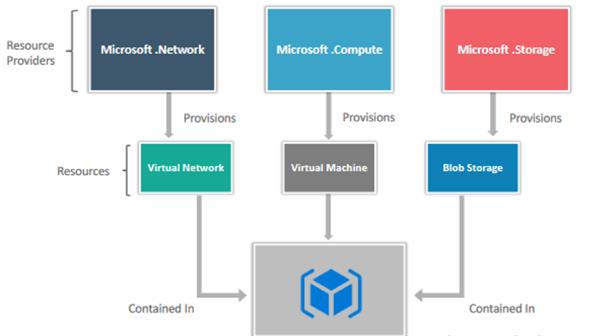
How Azure Resource Manager works
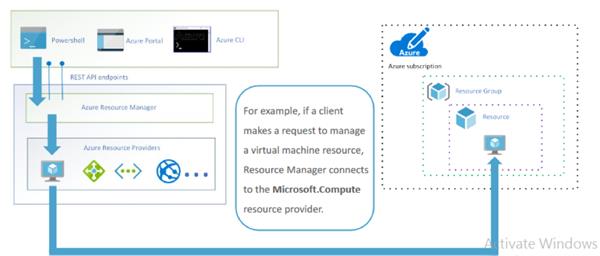
Azure policy
It is service that you use to create, assign and manage policies and they allow the organization to check which resources are compliant or not with the existing police
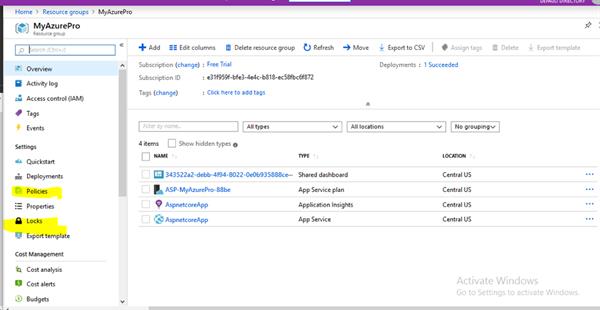
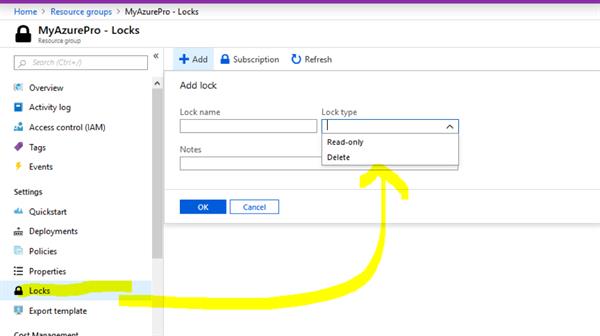
Azure Resource Management Locks :
It restricts operations on resources through this ARM locks
It helps you prevent accidental deletion or modification of your azure resources
That’s all for this post, I hope you enjoyed it and got the solution.